Federated Learning: Private & Collaborative AI for a Smarter Future

Introduction
Artificial Intelligence is fueled by data. The more data a model can learn from, the smarter and more capable it becomes. This has led to a data gold rush, with companies collecting vast amounts of user information to build the next generation of intelligent services. But this creates a fundamental paradox: how do we build powerful, helpful AI without compromising the personal data security and privacy of individuals? For years, the answer was, “We can’t.” You either sacrificed privacy for innovation or vice versa.
Enter Federated Learning, a groundbreaking approach that flips the traditional AI model on its head. Imagine training a powerful, global AI model with insights from millions of users without ever seeing their raw data. It sounds like magic, but it’s a powerful reality that is reshaping the future of AI privacy.
This is not just another technical buzzword. It’s a paradigm shift towards a more ethical, secure, and collaborative AI ecosystem. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll demystify federated learning, exploring how this decentralized machine learning technique works, its profound benefits, its real-world applications in healthcare and finance, and the challenges it still faces. Get ready to understand the technology that allows for powerful AI without data sharing, paving the way for a smarter, more private future.
The Data Privacy Dilemma: Why Traditional AI Falls Short
For decades, the standard practice in machine learning was simple: gather all the data in one place. Whether it was user photos, medical records, or financial transactions, the data was moved from its source to a centralized cloud server where a powerful AI model would be trained.
This centralized approach, while effective for model training, created a honeypot of sensitive information with significant risks:
- Massive Data Breaches: Centralized databases are prime targets for hackers. A single breach could expose the private information of millions of users.
- Erosion of User Trust: As people become more aware of how their data is being used, they are increasingly hesitant to share it, stifling the very innovation that data enables.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Regulations like Europe’s GDPR and California’s CCPA impose strict rules on data collection and processing, making the centralized model legally complex and costly.
- Data Sovereignty Issues: Data generated in one country may be legally prohibited from leaving its borders, preventing global collaboration.
This model fundamentally conflicts with the growing demand for AI data ownership and control. The need for a new method—one that respects privacy from the ground up—became overwhelmingly clear.
What is Federated Learning? Beyond the Buzzword
Federated Learning is a privacy-preserving AI technique that enables on-device AI training. Instead of bringing the data to the model (in a central server), federated learning brings the model to the data (on the user’s device).
Think of it like a team of expert chefs collaborating on a secret recipe. Instead of every chef sending their rare, private ingredients to a central kitchen, the master recipe is sent to each chef’s private kitchen. Each chef uses their local ingredients to improve the recipe and then sends back only their suggested improvements—not the ingredients themselves. The central kitchen then intelligently combines all the suggestions to create a much-improved master recipe, which is then sent back out for the next round of improvements.
In this analogy:
- The Chefs are the user devices (phones, laptops, hospital computers).
- The Local Ingredients are the user’s private data.
- The Master Recipe is the global AI model.
- The Suggested Improvements are the trained model updates (weights or gradients).
This process allows for a powerful, globally-trained AI model to be built from the collective experience of all devices, ensuring that sensitive raw data never leaves the user’s control. It’s the ultimate expression of secure machine learning.
How Federated Learning Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The elegance of federated learning lies in its distributed, cyclical process. While the technical details can be complex, the core workflow is beautifully logical. Let’s break down how this next-gen AI training method functions.
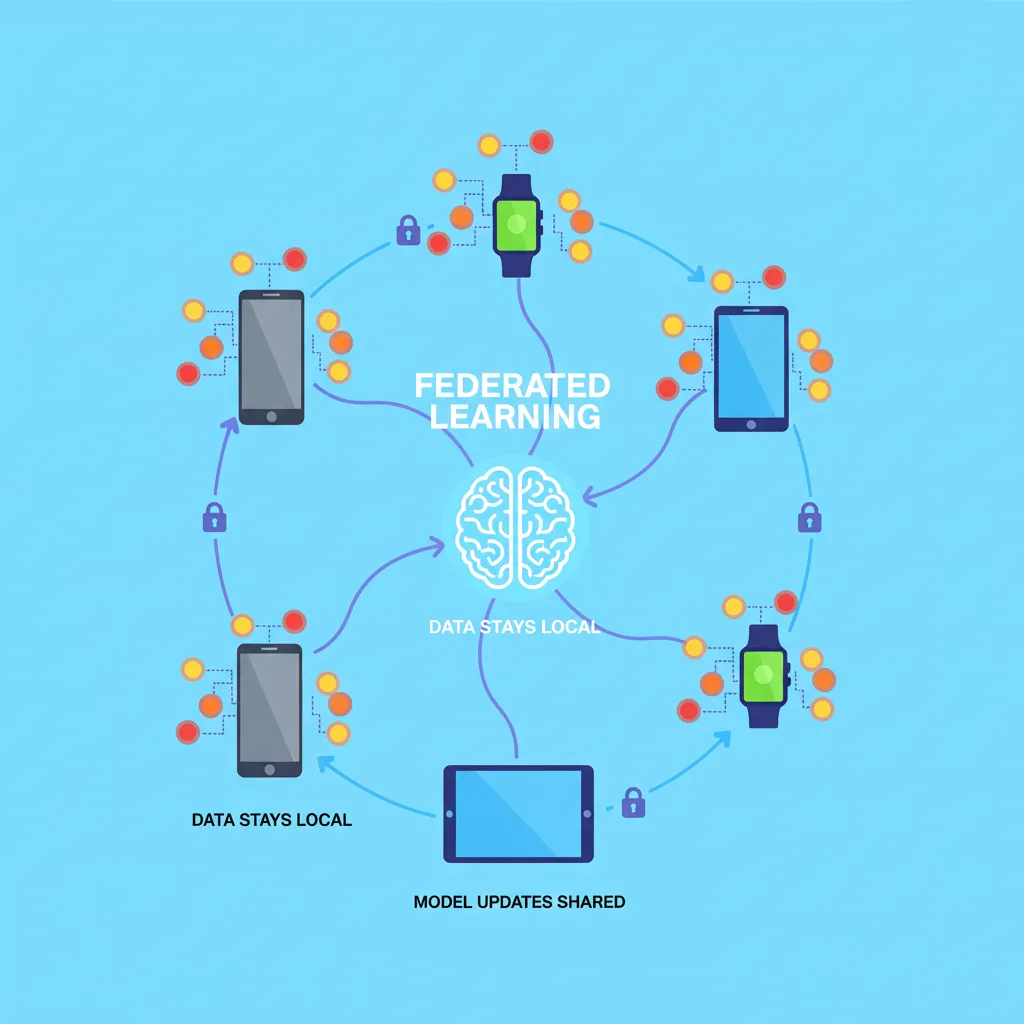
Step 1: Initialization & Distribution
It all starts with a central server or orchestrator. A data scientist creates an initial AI model (the “master recipe”). This generic global model is then sent out to hundreds, thousands, or even millions of decentralized edge devices, such as smartphones, IoT sensors, or computers within a hospital network.
Step 2: On-Device AI Training
Once the model arrives on a device, it begins training using the local data available only on that device. For example, your smartphone’s keyboard might use your typing history to improve its predictive text model, or a hospital’s server might use its local patient scans to refine a tumor detection model. This entire training process happens locally, respecting edge AI privacy and ensuring your data stays put.
Step 3: Encrypting and Sending Updates
After training locally, the device doesn’t send the data back. Instead, it generates a small, summarized update of what it learned. This update, typically consisting of model weights or gradients, represents the “suggested improvements” from our chef analogy. Critically, this update is encrypted and often further anonymized using techniques like differential privacy, which adds statistical “noise” to make it impossible to reverse-engineer the original data.
Step 4: Secure Aggregation
The central server receives these encrypted updates from many devices. It doesn’t need to decrypt them individually. Using a cryptographic technique called Secure Aggregation, the server can combine all the updates to calculate the average improvement. This process ensures that the central server only learns the collective result, not the contribution of any single device, providing a powerful layer of machine learning privacy.

Step 5: Improving the Global Model
The aggregated average update is then applied to the global model on the central server. This new, smarter version of the model has now learned from the collective experience of all participating devices without violating their privacy.
Step 6: Iteration
This is not a one-time event. The improved global model is sent back to the devices, and the entire process (Steps 2-5) repeats. With each round, the model becomes progressively more accurate and robust, achieving high performance through AI model collaboration.
The Unparalleled Benefits of a Decentralized Approach
The shift to a federated model offers transformative advantages that address some of the biggest challenges in AI ethics and logistics.
Championing Data Privacy and Security
This is the cornerstone benefit. By design, federated learning minimizes data collection. Raw, sensitive data remains on the user’s device, drastically reducing the risk of data breaches during transmission or from a central server. This approach is fundamental to building trustworthy AI systems and is a core component of privacy-enhanced machine learning. It empowers users with true AI data ownership.
Enabling True AI Model Collaboration
Federated learning breaks down data silos. Consider several hospitals that want to build a world-class cancer detection AI. None of them can legally or ethically share their patient data. With federated learning, they can collaboratively train a single, powerful model using all of their data combined, leading to a much more accurate diagnostic tool. This is a game-changer for healthcare AI federated learning and enables a level of global AI collaboration that was previously impossible. It’s the key to unlocking insights from AI for sensitive data.

Reducing Latency and Bandwidth Costs
Moving massive datasets to the cloud is slow and expensive. Federated learning is far more efficient. It only requires sending small model updates, saving significant network bandwidth. Furthermore, since the model runs on the device, it can provide real-time predictions and personalization without needing to communicate with a server, resulting in a faster, smoother user experience. This efficiency aligns with the principles of creating a more sustainable digital world. Related: Sustainable AI: Eco-Friendly Innovation for a Greener Digital Future
Powering Real-Time Personalization
Federated learning allows models to be personalized to you, on your device. The predictive text on your keyboard learns your unique slang and phrases, and your phone’s digital assistant gets better at recognizing your voice—all without sending your personal conversations or texts to the cloud. This delivers a highly customized experience while maintaining the highest level of privacy, and is a great example of how this technology can improve daily life. Related: Top AI Tools for Personalized Learning & Student Success
Federated Learning in Action: Real-World Applications
Federated learning is already being deployed across various industries, solving real-world problems that were once intractable.
Revolutionizing Healthcare AI
In healthcare, data is incredibly valuable but also incredibly sensitive. Federated learning allows medical institutions to train AI models for disease diagnosis, drug discovery, and patient risk prediction on a massive scale. A model can learn to detect diabetic retinopathy from retinal scans across thousands of hospitals globally without a single patient image ever leaving its original hospital network.
Securing the Future of Finance
Banks and financial institutions are using finance AI privacy techniques like federated learning to build more robust fraud detection systems. By training a model across different banks’ transaction data, they can identify new and complex fraudulent patterns much faster, all while keeping individual customer financial data completely private and secure. This collaborative approach can also be applied to credit scoring and understanding market trends. Related: Decoding Investor Psychology: How AI Can Tame Behavioral Biases
Building Smarter, More Private Cities
Smart city AI solutions rely on data from countless IoT devices, from traffic cameras to energy meters. Federated learning can optimize traffic flow, manage the energy grid, and predict infrastructure maintenance needs by learning from this distributed data. For example, it can build a city-wide traffic prediction model without ever tracking the specific movements of individual vehicles or people, balancing civic efficiency with personal privacy. This has exciting applications in areas like sustainable urban planning. Related: AI-Powered Urban Farming: Grow Smarter, Live Greener
Enhancing Your Smartphone Experience
You are likely already using federated learning every day. Google’s Gboard uses it to improve next-word prediction and emoji suggestions based on what you type on your phone. Apple uses it to improve “Hey Siri” voice recognition and scene detection in Photos. This on-device AI training makes your device smarter and more helpful without uploading your personal content.
Navigating the Challenges: Hurdles to Widespread Adoption
Despite its immense potential, federated learning is not a silver bullet. There are significant technical and logistical challenges that researchers and engineers are actively working to solve.
- Communication Overhead: While more efficient than sending raw data, the iterative process of sending model updates back and forth can still be communication-intensive, especially for complex models or networks with millions of devices.
- Data Heterogeneity (Non-IID Data): In a centralized system, data can be cleaned and balanced. In federated learning, the data on each device is different (Non-Independent and Identically Distributed). One person might type about sports, another about cooking. This statistical heterogeneity can bias the model and degrade its performance if not managed carefully.
- System Heterogeneity: The participating devices vary widely in terms of processing power, memory, battery life, and network connectivity. A robust federated learning system must be able to handle devices that are slow, offline, or drop out of the training process unexpectedly.
- Security and Privacy Threats: While federated learning protects raw data, it introduces new potential attack surfaces. Malicious actors could try to poison the global model by sending intentionally corrupt updates. Advanced attackers might also attempt “inference attacks” to try and deduce information about a device’s private data from its model updates, which is why additional protections like differential privacy are crucial.
The Future of AI is Collaborative and Private
Federated learning represents a fundamental pillar in the construction of a more responsible, ethical, and effective AI ecosystem. It is a key enabler of the future of AI privacy and is becoming a foundational technology for any organization serious about deploying AI with sensitive data.

Looking ahead, we’ll see enterprise federated learning platforms become more common, making it easier for businesses to deploy this technology. We will also see its integration with other privacy-enhancing technologies, like blockchain for creating immutable audit trails of model training and homomorphic encryption for computing on encrypted data.
This technology isn’t just about defense; it’s about offense. It unlocks new possibilities for global AI collaboration to solve humanity’s biggest challenges—from curing diseases to fighting climate change—by pooling our collective knowledge without sacrificing our individual privacy. It’s a move towards an AI that isn’t just intelligent, but also respectful. Related: What is GPT-4o? The Ultimate Guide to Real-Time AI
Conclusion
We stand at a crossroads in the development of artificial intelligence. The old way of centralizing data created incredible tools but at a great cost to privacy and security. Federated learning offers a new path forward—a path where innovation and privacy are not mutually exclusive.
By bringing the model to the data, this decentralized machine learning approach allows us to build smarter, more personalized, and more efficient AI systems securely and ethically. It addresses the core tenets of AI ethics data handling by embedding privacy into the very architecture of the training process. From the smartphone in your pocket to the advanced diagnostic tools in hospitals, federated learning is quietly powering a revolution.
The future of AI will not be built in a single, massive data center. It will be built collaboratively, across a distributed network of devices, organizations, and individuals, all working together to create intelligence while preserving the fundamental right to privacy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is federated learning in simple terms?
In simple terms, federated learning is a way to train a shared AI model across many different devices without the data ever leaving those devices. Instead of collecting everyone’s data in one place, the AI model is sent to each device to learn locally, and only the learning summaries are sent back and combined to improve the main model.
Q2. What is the main advantage of federated learning?
The main advantage is privacy. Because raw, sensitive data never leaves the local device (like your phone or a hospital’s server), it significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and protects user confidentiality. This allows for powerful AI model collaboration even with highly sensitive data.
Q3. Who uses federated learning?
Major technology companies are prominent users. Google uses it for its Gboard keyboard to improve predictions. Apple uses it to enhance Siri’s voice recognition and other on-device intelligence features. It is also seeing rapid adoption in industries like healthcare, finance, and automotive manufacturing.
Q4. Is federated learning secure?
Federated learning is significantly more secure than traditional centralized machine learning regarding raw data privacy. However, it’s not immune to all threats. Advanced security measures like Secure Aggregation and Differential Privacy are often added to protect against attacks like model poisoning or attempts to infer data from the model updates.
Q5. What is the difference between federated and distributed learning?
While both involve training across multiple machines, their primary goals differ. Distributed learning’s main goal is to speed up training by parallelizing the process, and it assumes the data is trusted and can be freely distributed across nodes in a data center. Federated learning’s primary goal is to train on data that cannot be moved due to privacy, and it is designed to work with untrusted, heterogeneous devices over potentially slow networks.
Q6. Can federated learning work without an internet connection?
The on-device training part of federated learning can happen entirely offline. However, an internet connection is required periodically to download the latest global model from the central server and to upload the local model’s encrypted updates. The process is often designed to happen only on unmetered connections (like Wi-Fi) and when the device is charging to minimize impact.