Depin & The Future of Energy: Decentralized Power for a Sustainable World

Introduction
For over a century, our world has been powered by a silent, sprawling giant: the centralized energy grid. It’s a marvel of 20th-century engineering, but in the 21st century, it’s showing its age. Prone to blackouts, slow to adopt renewables, and often leaving consumers with little choice or control, this old model is straining under the weight of modern demands and a changing climate. But what if we could build a new grid from the ground up? A smarter, cleaner, more resilient system owned and operated by the people it serves?
This isn’t a far-off futuristic dream. It’s the promise of Depin, or Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks. By merging the physical world of energy hardware with the digital worlds of blockchain and crypto-economics, Depin is creating a paradigm shift in how we generate, store, and distribute power. It’s a movement that’s transforming passive energy consumers into active participants in a vibrant, decentralized energy market.
In this deep dive, you’ll discover the core principles of Depin energy, explore how it’s fixing the critical flaws of our current system, and see the incredible Depin use cases—from peer-to-peer energy trading in your neighborhood to community-owned microgrids that offer true energy independence. We’ll unpack the technology, weigh the benefits, and cast a vision for a sustainable world powered by a truly decentralized grid.
The Gridlock: Why Our Centralized Energy System is Overloaded
Before we plug into the solution, it’s crucial to understand the problem. The traditional power grid is a one-way street. Large, centralized power plants—often burning fossil fuels—generate electricity that is pushed across vast distances through transmission lines to homes and businesses. This model has several fundamental weaknesses.
- Inefficiency and Waste: A significant amount of energy is lost as heat during long-distance transmission. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, about 5% of the electricity transmitted and distributed in the United States is lost annually.
- Vulnerability: Centralization creates single points of failure. A storm, cyberattack, or equipment failure at a major plant or substation can trigger cascading blackouts affecting millions.
- Barriers to Renewables: The grid was designed for a constant, predictable power supply. The intermittent nature of solar and wind power creates challenges for grid operators, slowing the transition to green energy Depin solutions.
- Lack of Consumer Control: As a consumer, you have almost no say. You can’t choose where your energy comes from, and you can’t easily sell the excess power your rooftop solar panels generate back to your neighbors. You are a price taker, not a market participant.
This rigid, top-down structure is simply not equipped for the dynamic energy landscape of the future—a future that demands flexibility, resilience, and a rapid shift towards sustainable energy solutions.
Enter Depin: A New Dawn for Energy Infrastructure
Depin flips the traditional model on its head. Instead of a few large entities controlling the infrastructure, Depin uses blockchain technology and token incentives to crowdsource the creation and operation of physical networks.
What Exactly are Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks?
At its core, Depin technology explained is a simple but powerful idea: let a community of users collectively build and manage infrastructure they all need. It coordinates millions of individual devices—from solar panels and home batteries to smart thermostats and EV chargers—and allows them to work together as a cohesive, intelligent network.
Think of it like Airbnb or Uber, but for physical hardware. Instead of a single company owning all the cars or properties, individuals contribute their own assets to a network and are rewarded for it. In the energy sector, this means you can be rewarded for contributing your home battery’s storage capacity or your solar panel’s excess generation to help stabilize the local grid. This is the foundation of Web3 energy.
The Three Pillars of a Depin Energy Network
A Depin energy system is built on three interconnected layers that work in harmony:
- Physical Infrastructure (The Hardware): This layer consists of Distributed Energy Resources (DERs). These are the small-scale power generation and storage units owned by individuals and businesses: rooftop solar panels, home batteries (like the Tesla Powerwall), smart appliances, and electric vehicle chargers.
- Blockchain Technology (The Digital Trust Layer): This is the decentralized, transparent, and immutable ledger that records every transaction on the network. It automates agreements (via smart contracts) and ensures that when you sell a kilowatt-hour of energy to your neighbor, the transaction is secure, verifiable, and executed without needing a traditional utility company as a middleman.
- Token Incentives (The Economic Engine): This is the secret sauce that motivates participation. By contributing resources to the network—whether it’s energy, storage, or even data—participants earn tokens. This energy tokenization creates a powerful economic flywheel: the more people participate, the more robust and valuable the network becomes, which in turn increases the value of the rewards.
How Depin is Rewiring the Future of Power
By combining these three pillars, Depin unlocks powerful new capabilities that are impossible in the old centralized system. It’s creating the foundation for truly smart grids and a more democratic energy future.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Energy Trading: Your Neighbor, Your Power Company
Imagine your rooftop solar panels generate more electricity than your home can use on a sunny afternoon. Instead of selling that excess power back to the utility for a low, fixed rate, what if you could sell it directly to your neighbor down the street who needs to charge their electric vehicle?
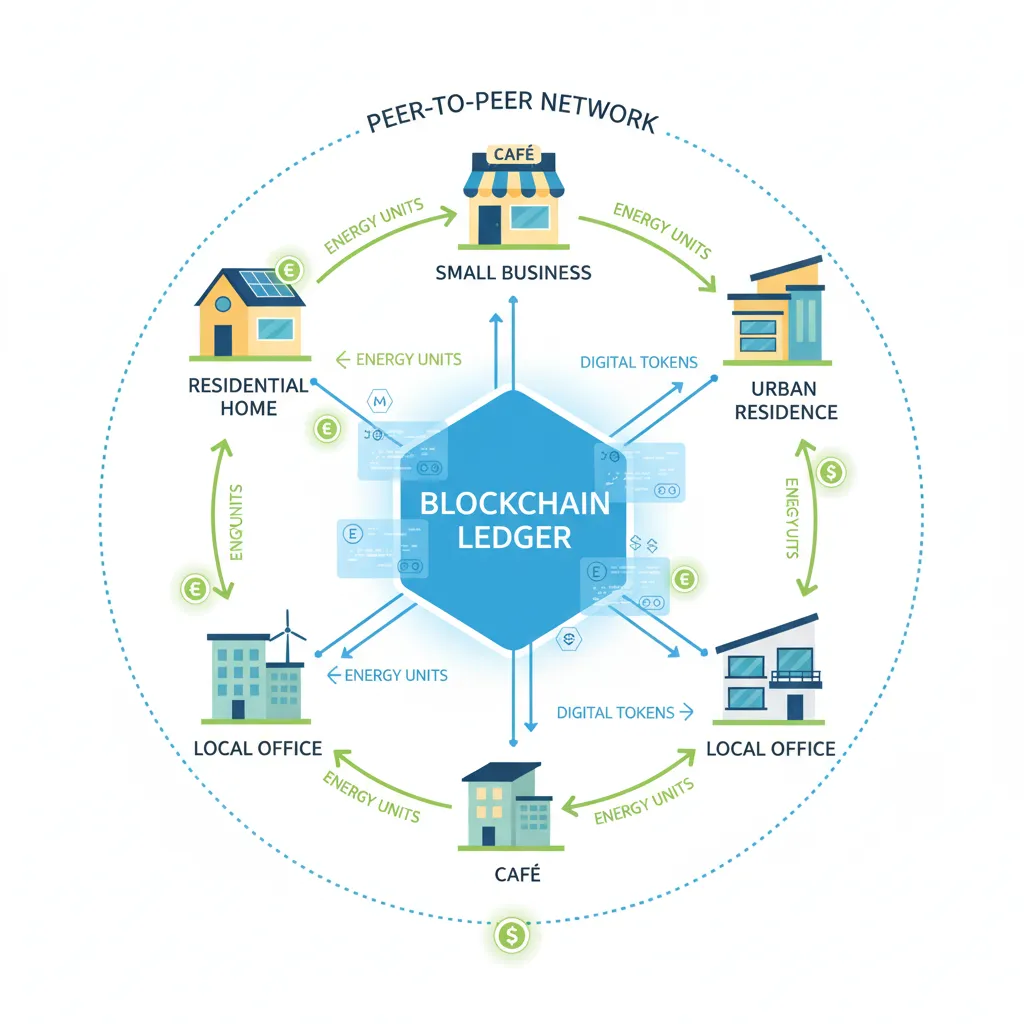
This is peer-to-peer energy trading, a cornerstone use case of Depin energy. A blockchain-based platform acts as a secure marketplace where producers and consumers can trade energy directly. Smart contracts automatically handle the transaction, ensuring the producer gets paid instantly and the consumer receives the electricity.
The benefits are transformative:
- Producers (Sellers): Earn a better price for their excess renewable energy.
- Consumers (Buyers): Access locally generated, clean energy, often at a lower cost than utility rates.
- The Grid: Localizing energy consumption reduces strain on the larger transmission network.
Building Resilient Community Power Networks with Microgrids
A microgrid is a self-sufficient energy system that serves a discrete geographic area, like a college campus, hospital complex, or a residential neighborhood. While traditional microgrids often rely on a central controller, microgrids blockchain integration takes them to the next level.
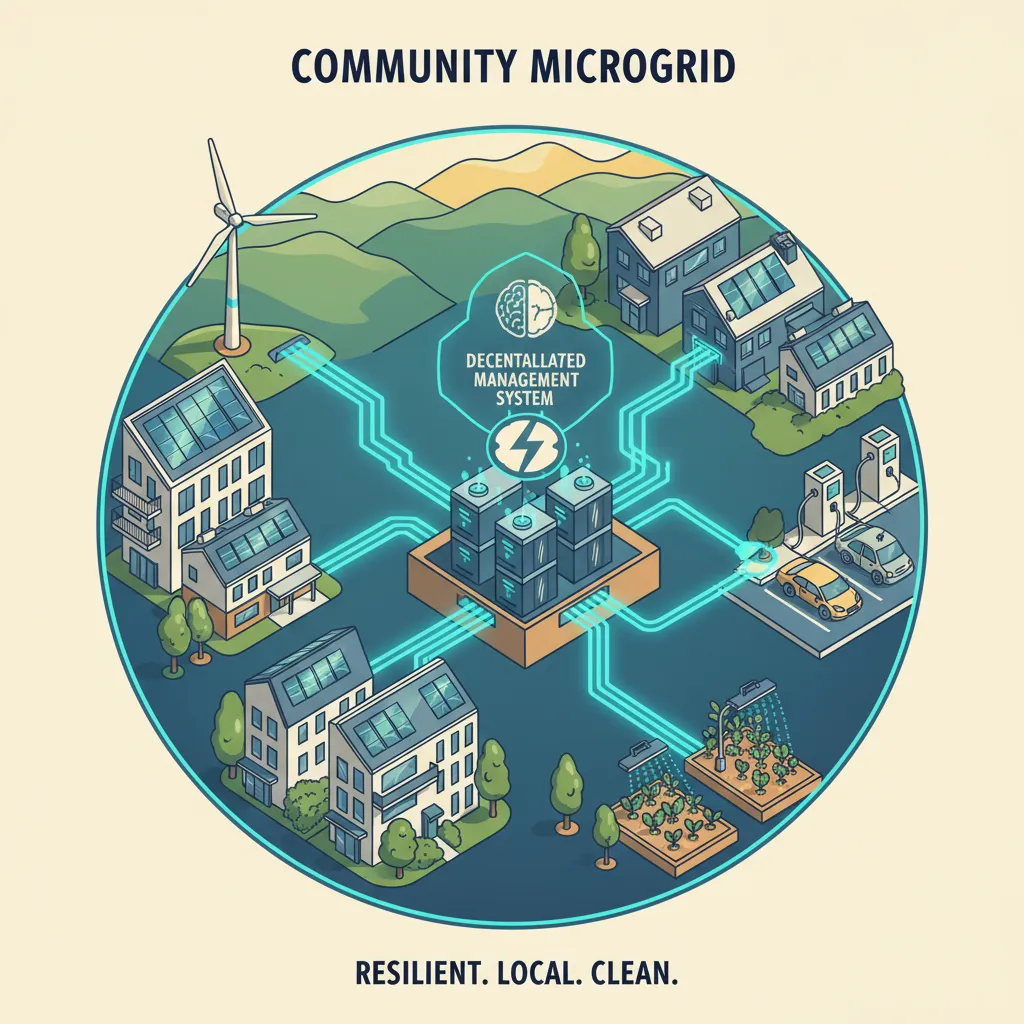
Depin enables the creation of community power networks that are truly decentralized. The blockchain coordinates all the DERs within the microgrid, balancing energy loads, managing storage, and facilitating P2P trading. Most importantly, these microgrids can operate independently from the main grid. If a storm knocks out power to the wider region, the community microgrid can “island” itself and keep the lights on for its members, providing an unprecedented level of resilience and energy independence solutions. Related: The Role of AI Agents in Creating Sustainable Smart Homes
Smart Grids and AI-Powered Energy Efficiency
The future of energy isn’t just about decentralizing generation; it’s about making the grid intelligent. Depin networks generate a massive amount of real-time data from millions of connected devices. This data is the fuel for AI algorithms that can optimize the entire system for maximum energy efficiency.
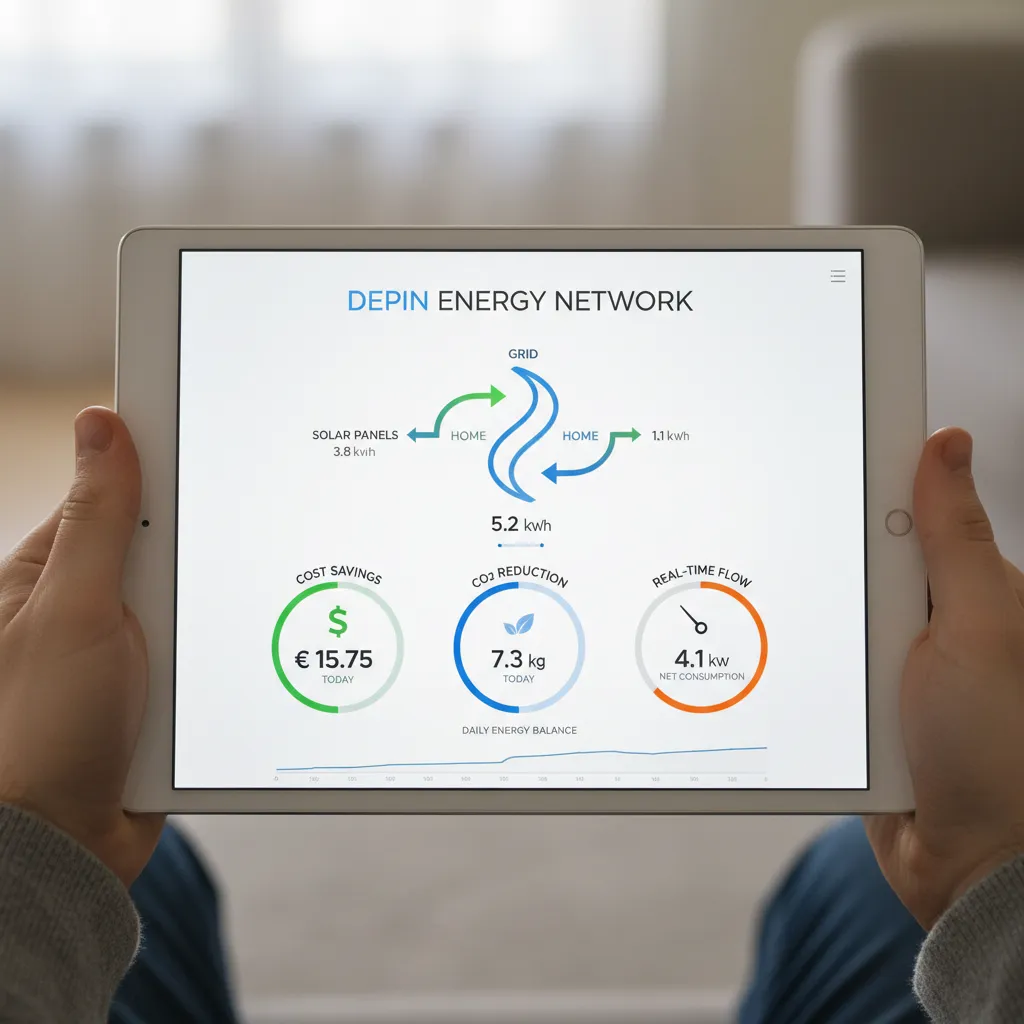

An AI-powered smart grids Depin can:
- Predict Demand: Forecast energy needs with high accuracy based on weather, time of day, and community events.
- Balance Loads: Automatically instruct batteries to charge when energy is cheap and abundant (e.g., midday solar peak) and discharge when demand is high and supply is low.
- Prevent Outages: Identify potential stress points in the network and reroute power to prevent failures before they happen.
- Optimize EV Charging: Coordinate electric vehicle charging across a neighborhood to avoid overloading the local grid during peak hours.
This level of granular control and optimization promises a future with less energy waste and more reliable power for everyone.
The Tangible Benefits of Energy Decentralization
The impact of Depin on energy is not just theoretical. It offers concrete advantages for every stakeholder, from individual homeowners to the planet itself.
For the Planet: Accelerating the Green Transition
One of the most significant Depin network advantages is its ability to supercharge the adoption of renewables. By creating a direct financial incentive (token rewards) for installing solar panels and batteries, Depin makes sustainable infrastructure investment accessible to everyone, not just large corporations. This grassroots approach can dramatically accelerate the build-out of renewable energy infrastructure and foster clean energy innovation.
For the Consumer: Empowerment, Savings, and Independence
Depin shifts power—both literally and figuratively—into the hands of consumers.
- Lower Bills: By participating in P2P energy trading and optimizing consumption, users can significantly reduce their energy costs.
- New Income Streams: Homeowners with solar panels or batteries can earn passive income by selling their excess capacity to the network.
- Greater Control: Users gain transparency and control over their energy usage and data, a critical aspect of energy data privacy.
- Energy Independence: Being part of a resilient microgrid means less reliance on a fragile, centralized system.
For the Grid: Enhanced Stability and Security
Contrary to concerns about chaos, a well-designed decentralized system is more robust than a centralized one. By distributing generation and storage, Depin reduces the risk of large-scale blackouts. The failure of one node (e.g., a home’s solar inverter) has a negligible effect on the overall network, which can intelligently reroute power and self-heal.
For Investors: A New Frontier in Climate Tech
Depin represents a groundbreaking model for renewable energy financing. It opens up climate tech investment to a global pool of capital through tokenization. Investors can directly fund the development of community solar projects or other sustainable tech trends and receive a direct return based on the project’s success, democratizing access to an asset class that was previously reserved for institutional players.
The Road Ahead: Overcoming Challenges on the Path to Adoption
While the vision is compelling, the path to a fully decentralized energy future has its hurdles.
- Navigating Regulatory Landscapes: The energy sector is heavily regulated, and current laws were written for a centralized world. Policymakers and regulators need to adapt to accommodate new models like P2P trading and community-owned microgrids.
- Ensuring Scalability and Interoperability: For Depin to work on a global scale, different projects and protocols must be able to communicate with each other. Establishing common standards is essential for a seamless, interconnected network.
- Protecting Energy Data Privacy: Smart meters and IoT devices collect sensitive data about household energy consumption. Ensuring this data is secure and user-controlled is paramount to building trust. Blockchain’s cryptographic security offers a strong foundation, but robust governance models are still needed. Related: AI City Surveillance: Navigating the Balance Between Safety and Privacy Rights
The Vision: A Glimpse into a Depin-Powered World
Close your eyes and imagine a city in 2035. The rooftops are a mosaic of solar panels. Electric vehicles are parked in driveways, not just drawing power but also acting as mobile batteries, feeding energy back into the grid during peak demand.

Your home’s AI-powered energy agent, connected to the local Depin network, runs your life with perfect efficiency. It charges your car overnight when electricity prices are lowest. It sells your excess solar power to the local school in the afternoon for a premium. When a heatwave puts a strain on the regional grid, your community’s microgrid seamlessly disconnects, and your lights don’t even flicker. You check your energy dashboard and see you’ve not only covered your own electricity bill but also earned a small profit.
This isn’t science fiction. This is the world that decentralized power systems are making possible.
Conclusion
Depin is more than just a niche application of blockchain technology; it is a fundamental re-imagining of our relationship with energy. It’s a powerful convergence of sustainable energy solutions, decentralized finance, and community empowerment. By dismantling the centralized, monolithic structures of the past, we can build a future of power grids that are more resilient, efficient, democratic, and, crucially, sustainable.
The transition won’t happen overnight, but the movement is gaining momentum. As more individuals, communities, and innovators embrace the principles of Depin energy, we move closer to a future where clean, reliable power is a fundamental right, not a centrally-controlled commodity. The power to build this sustainable world is, quite literally, being placed back in our hands.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is Depin in the energy sector?
Depin (Decentralized Physical Infrastructure Networks) in the energy sector is an approach that uses blockchain technology and token incentives to build and operate a decentralized power grid. Instead of relying on large, central utility companies, Depin enables individuals and communities to contribute their own energy resources, like rooftop solar panels and batteries, to a shared network and be rewarded for their participation.
Q2. How does peer-to-peer energy trading work?
Peer-to-peer (P2P) energy trading allows a person generating excess electricity (e.g., from solar panels) to sell it directly to another consumer in their community. This is facilitated by a blockchain platform that acts as a secure marketplace. Smart contracts automate the transaction, ensuring the seller gets paid and the buyer receives the power, all without a traditional utility acting as a middleman.
Q3. What role does blockchain play in Depin energy?
Blockchain serves as the trust layer for a Depin energy network. It provides a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger to record all energy transactions. It also enables smart contracts, which are self-executing agreements that automate processes like P2P trading and payments, ensuring the system operates fairly and efficiently without a central authority.
Q4. What are the main benefits of a decentralized power system?
The primary benefits include increased grid resilience (less vulnerability to large-scale blackouts), greater efficiency by reducing energy loss over long distances, empowerment for consumers who can become producers (prosumers) and earn income, and the acceleration of renewable energy adoption by creating direct financial incentives for individuals to invest in green technology.
Q5. Are there real-world examples of Depin energy projects?
Yes, several projects are pioneering this space. For example, projects are building networks that allow users to connect renewable energy devices, share power, and earn rewards. These platforms demonstrate the viability of using token incentives to bootstrap community-owned energy infrastructure and create vibrant, localized energy markets.
Q6. Is Depin a good investment for sustainable infrastructure?
Depin presents a novel and compelling model for sustainable infrastructure investment. By tokenizing energy assets, it allows for more fluid, global, and democratized renewable energy financing. It enables investors to directly fund green projects and potentially earn returns from real-world energy production, aligning financial incentives with positive environmental impact and supporting climate tech investment trends.
Q7. What is the difference between Depin and traditional renewable energy projects?
Traditional renewable projects, like large solar or wind farms, are typically centrally owned and financed by large corporations or governments. They feed power into the existing centralized grid. Depin energy projects are decentralized and community-driven. They focus on coordinating thousands of small, individually-owned distributed energy resources (DERs), creating a bottom-up power grid owned and operated by its users.